There seems to be nothing in your cart.
Didn't find what you were looking for? Contact our consultant.
To save your shopping cart until your next visit, create an account or register .
Browse our Hits sales
There seems to be nothing in your cart.
Didn't find what you were looking for? Contact our consultant.
To save your shopping cart until your next visit, create an account or register .
Browse our Hits sales
*This text is provided for informational purposes only. The information given by the author is his own development using information from publicly available sources. The company is not responsible for the author's material presented.
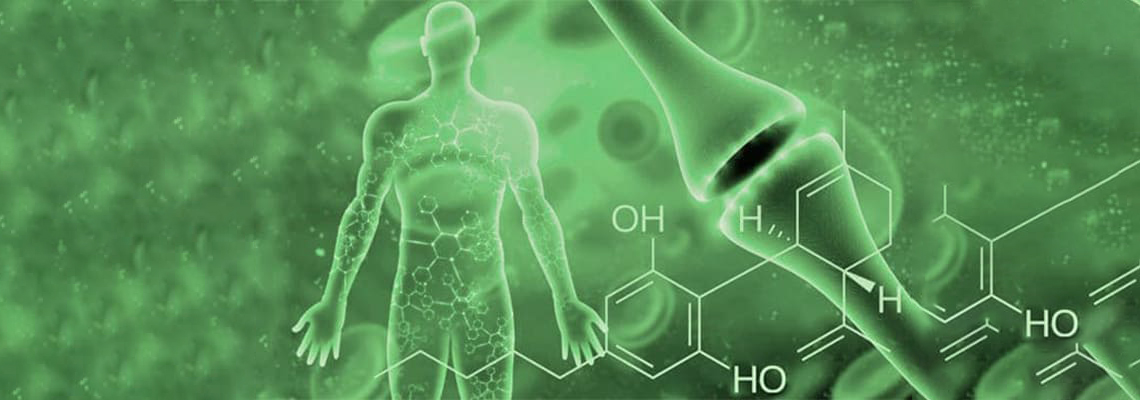
What really happens when you use cannabis? Many users are aware of its profound effect on the human body, but few understand how it manifests itself. The chemical compounds of cannabis affect the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is responsible for maintaining homeostasis (stable state) of the body.
Researchers estimate that ECS evolved in animals over 600 million years ago. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are found in the brain, organs, connective tissue, glands, and immune cells throughout the body. This system is responsible for managing a wide range of physiological processes, including mood, memory, pain, appetite, and the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
To better understand this definition, first, let's figure out what the endocanabinoid system consists of, and then we'll talk about each receptor separately, its functions, how it works and how it affects the human body.
The endocannabinoid system was first discovered by a US government-funded team in 1988. They discovered a unique type of receptor that responded to cannabis extract and named it CB1.
Following this discovery, research into the endocannabinoid system skyrocketed. Pfizer's pharmaceutical team created an analog of THC that allowed scientists to spot a compound with radionuclides and map the location of those receptors. This led to the discovery that there are far more endocannabinoid receptors in the brain than any other type of neurotransmitter, and also helped researchers discover a second type of endocannabinoid receptor called the CB2 receptor.
In 1992, the endogenous (produced by the body) cannabinoid neurotransmitter interacting with endocannabinoid receptors was uncovered by the efforts of three scientists, Rafael Mechoulam, William Dewan and Dr. J. Lumir Hanush. What they discovered was eventually named anandamide (from the Sanskrit word for bliss).
Scientists have been able to identify three key elements that make up the endocannabinoid system. These are endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors and enzymes.
The endocannabinoid system consists of two main receptors: CB1 and CB2. They can be found on many cells in our body. Various cannabinoids (endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids) bind to these receptors, block or modulate their activity. Scientists also believe that TRPV1 is part of the network since CBD, THC and anandamide can bind to it.
Author: Sergey Esipov
Related articles: